Subnets
Subnets
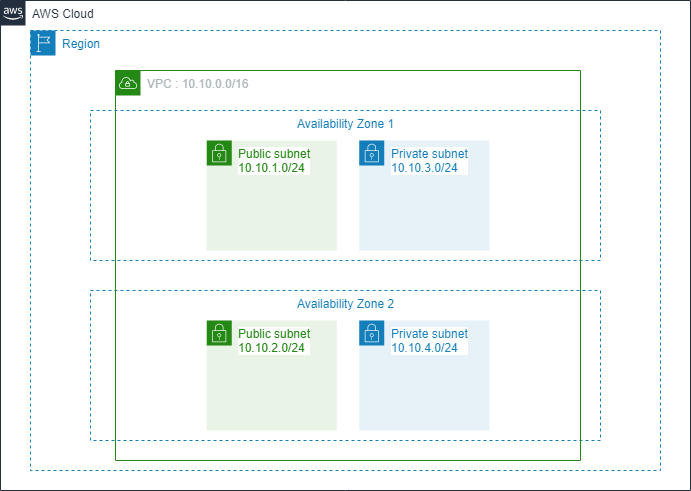
A subnet is a segment of the IP address range that you use when provisioning your Amazon VPC. It directly provides the active network range to the AWS resources that may run within it, such as Amazon EC2 and Amazon RDS (Amazon Relational Database Service). Subnets are identified through CIDR blocks (e.g., 10.0.1.0/24 and 192.168.0.0/24), and the subnet’s CIDRs must be within the VPC’s CIDR. The smallest subnet that can be created is /28 (16 IP addresses). AWS reserves the first 4 IP addresses and the last 1 IP address of each subnet for intranet networking purposes. For example, a /28 subnet has 16 available IP addresses, but 5 reserved IPs are used for AWS, leaving 11 usable IP addresses for resources operating within this subnet.
An Availability Zone (AZ) is a single or multi-data center located within a Region and identified based on geographical location. Within an AZ, there can be one or more subnets. However, a subnet can only reside in a single AZ and cannot extend to other AZs.
Subnets are categorized as:
- Public subnet: This subnet has a route table (discussed later) that directs traffic within the subnet to the VPC’s Internet Gateway (IGW) (discussed later).
- Private subnet: The opposite of a Public subnet, it lacks a route table directing traffic to the VPC’s IGW.
- VPN-only subnet: This subnet has a route table that directs traffic to Amazon VPC’s Virtual Private Gateway (VPG) (discussed later).
Regardless of the subnet type, the subnet’s internal IP address range is always private. This means that it is not possible to directly connect to addresses within this range from outside the Internet.