Internet Gateway
Understanding Internet Gateways
ℹ️ What is an Internet Gateway?
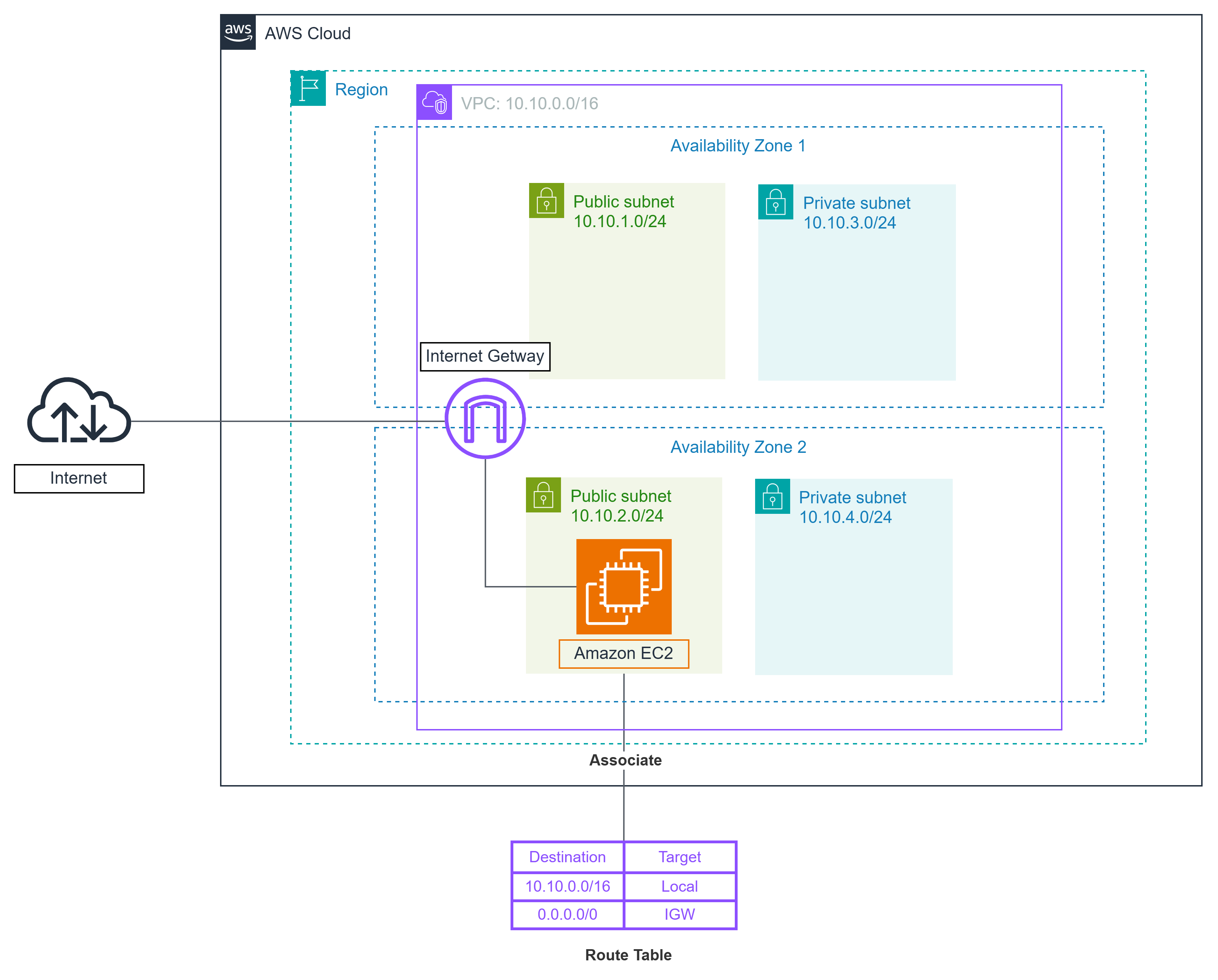
An Internet Gateway (IGW) is a horizontally scaled, redundant, and highly available VPC component that enables communication between your VPC resources and the internet. It serves as the entry and exit point for internet traffic to and from your VPC.
How Internet Gateways Work
Internet Gateways perform two essential functions:
- Route Table Integration - IGWs serve as a target in your VPC route tables for internet-bound traffic
- Network Address Translation (NAT) - IGWs perform network address translation for instances with public IP addresses
⚠️ Important Considerations
EC2 instances in your VPC only recognize their private IP addresses. When these instances send traffic to the internet, the IGW transparently translates the source private IP to the instance’s public IP address (or Elastic IP address).
Traffic Flow Through an Internet Gateway
When traffic flows through an Internet Gateway:
- Outbound Traffic: The IGW translates the instance’s private IP to its public IP using a one-to-one mapping
- Inbound Traffic: The IGW translates the destination public IP address back to the instance’s private IP address before forwarding traffic into the VPC
🔒 Security Note
For an EC2 instance to communicate with the internet, it must be in a subnet with a route table that has a route to the internet gateway, and it must have a public IP address or Elastic IP address.
💡 Pro Tip
Internet Gateways have no bandwidth constraints and do not charge for data transfer. You only pay for the data that passes through them based on standard AWS data transfer rates.