Create Subnet
Creating Subnets in Your VPC
ℹ️ What are Subnets?
Subnets are segments of a VPC’s IP address range where you can place groups of isolated resources. They allow you to organize your network architecture into public subnets (internet-accessible) and private subnets (internal only) across multiple Availability Zones for high availability.
Step-by-Step Subnet Creation
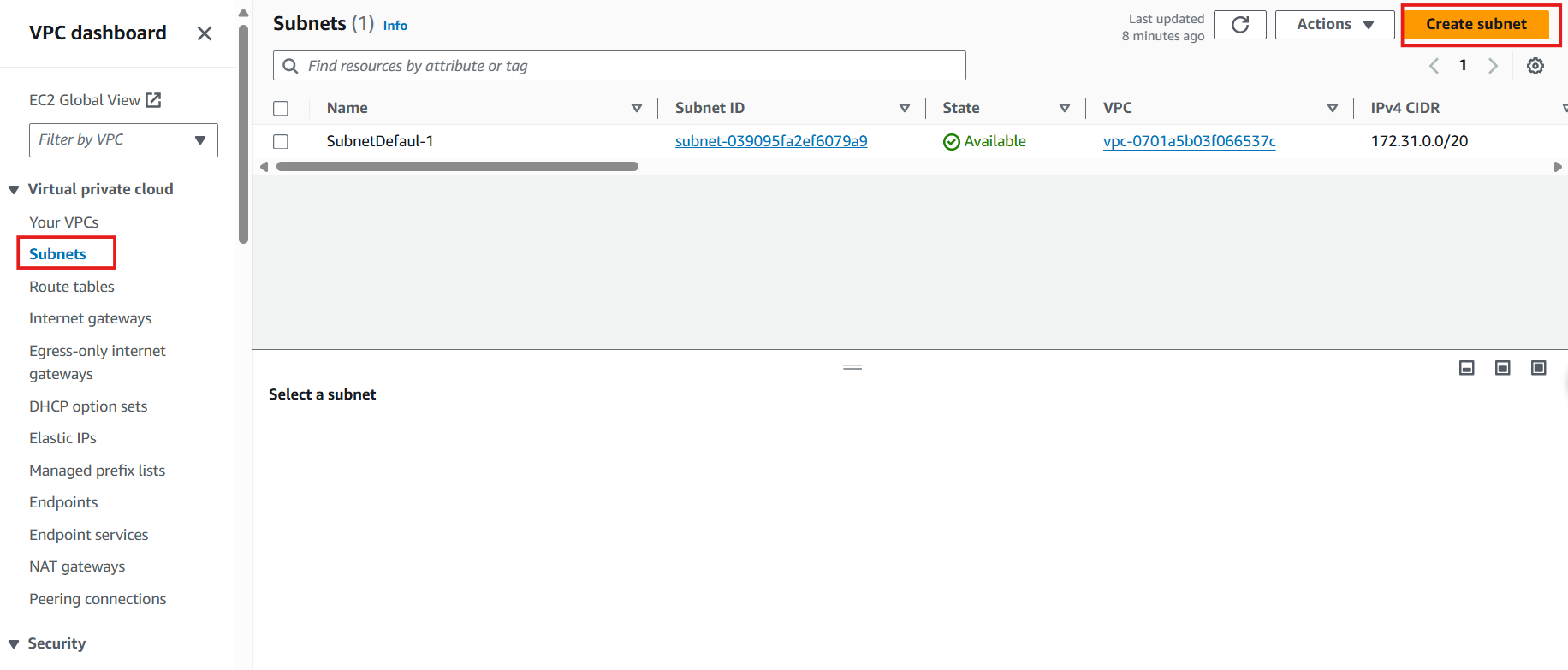
- Access the subnet creation interface:
- Navigate to the VPC console
- Select Subnets from the left navigation panel
- Click Create subnet
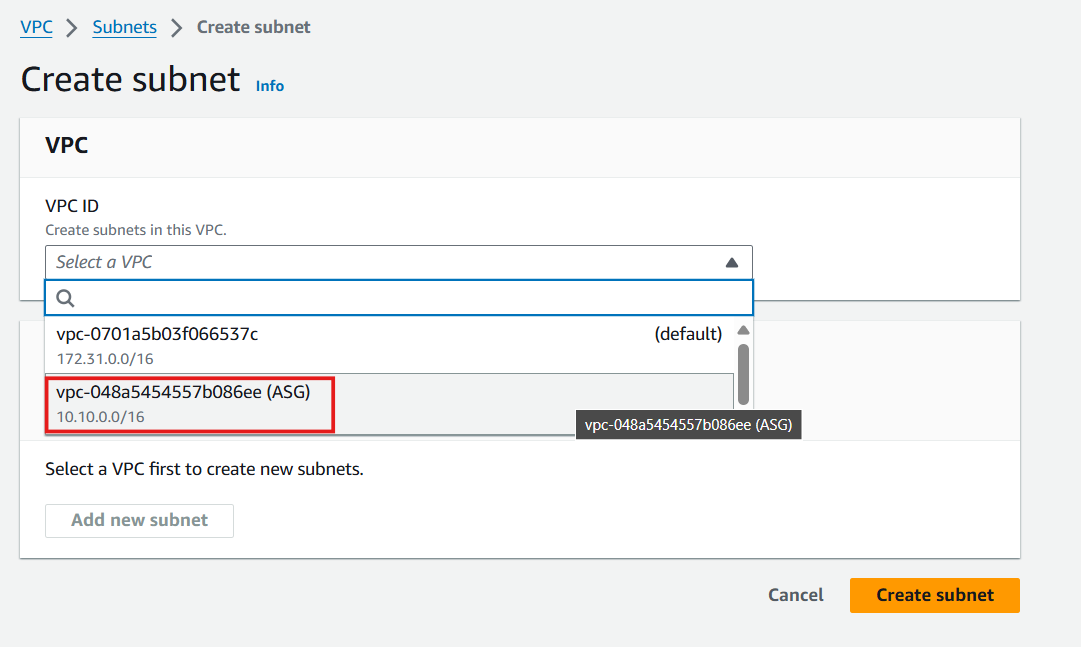
- Select your VPC:
- In the Create subnet interface, select the ASG VPC from the dropdown
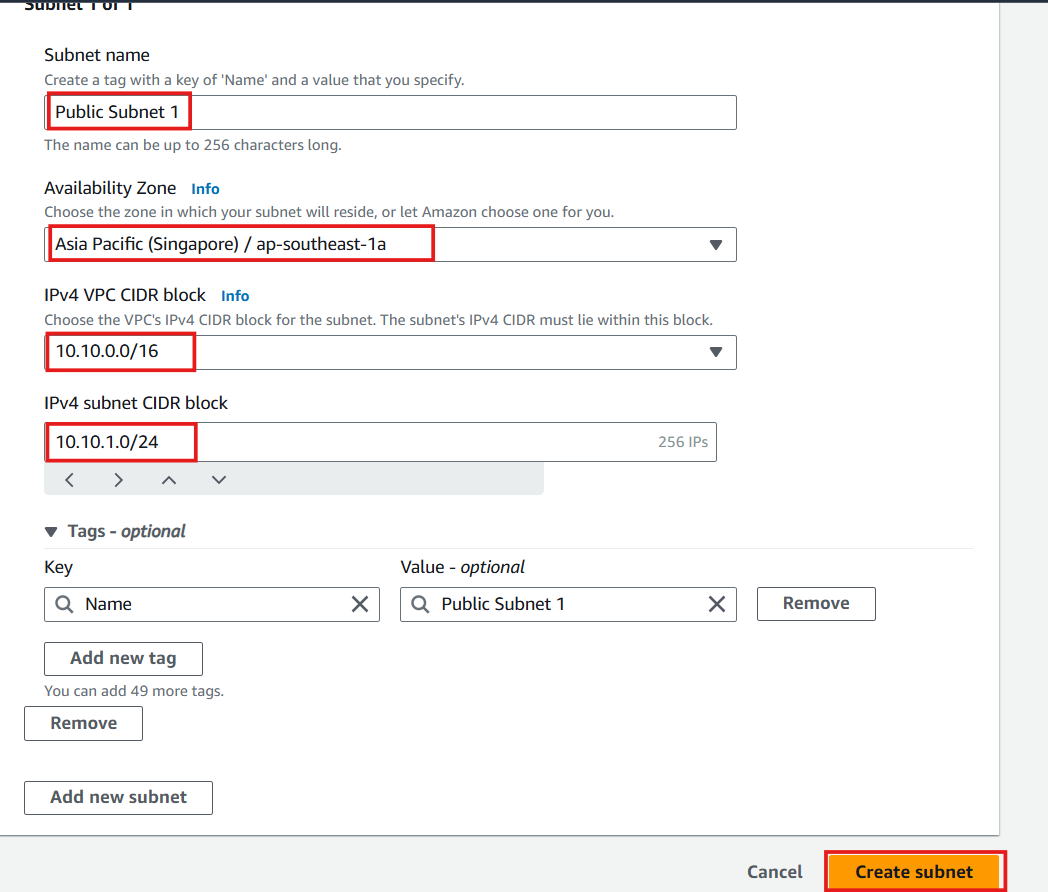
- Configure your first public subnet:
- Subnet name: Enter
Public Subnet 1 - Availability Zone: Select ap-southeast-1a
- IPv4 CIDR block: Enter
10.10.1.0/24(providing 256 IP addresses) - Click Create subnet
- Subnet name: Enter
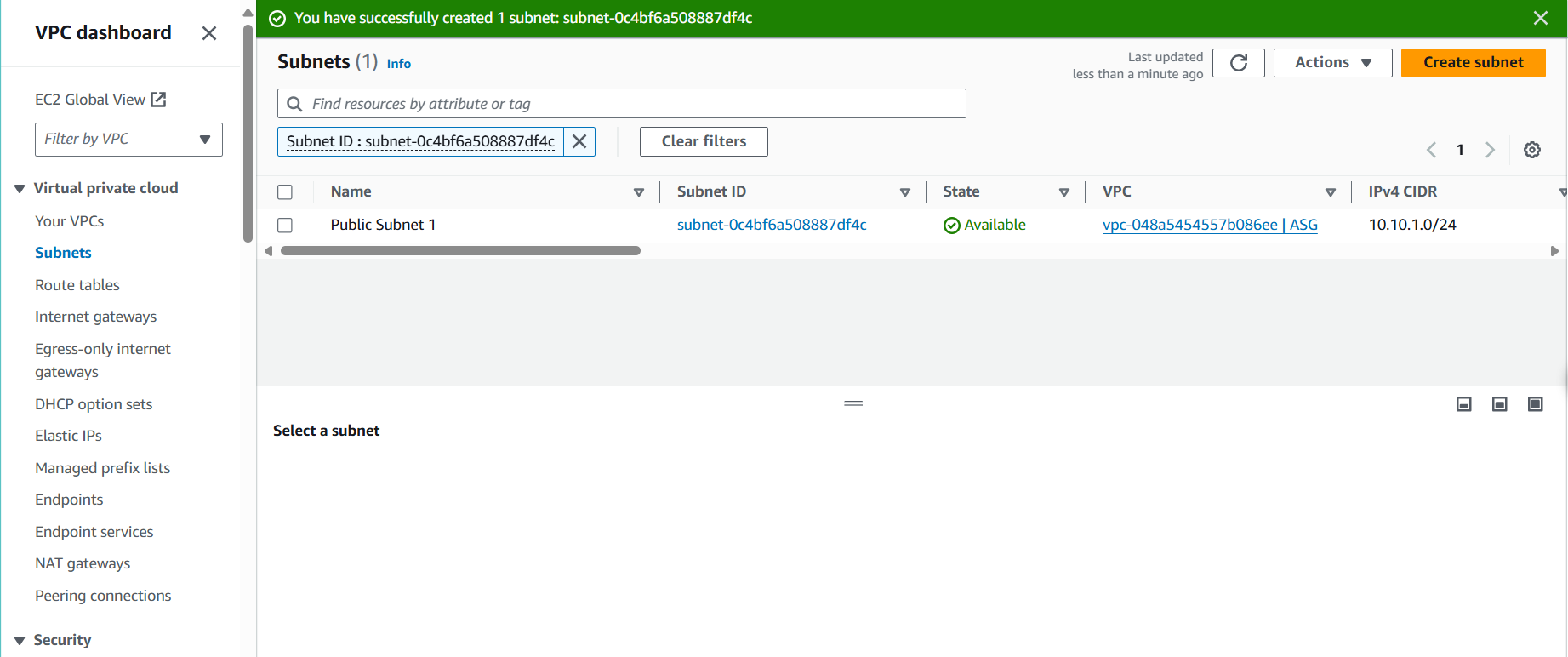
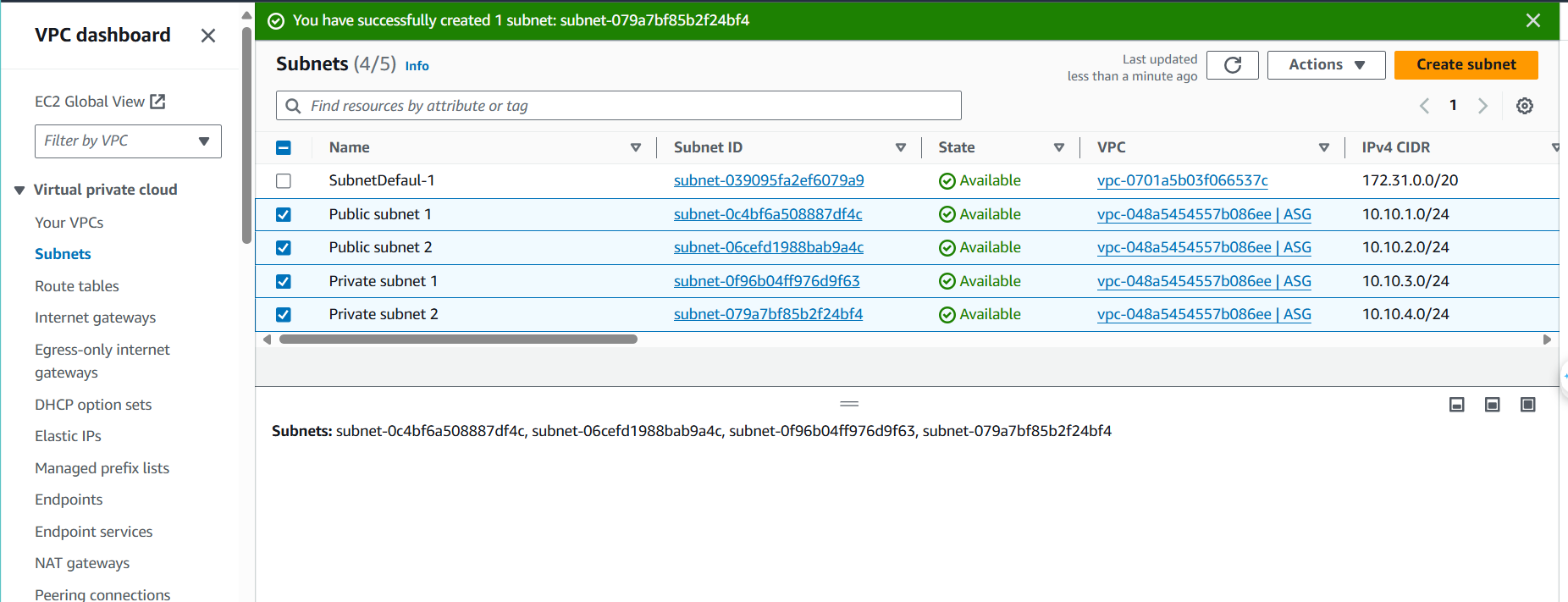
- Verify successful subnet creation:
- You should see a success message
- Your new subnet will appear in the subnet list
- Create additional subnets following the same process:
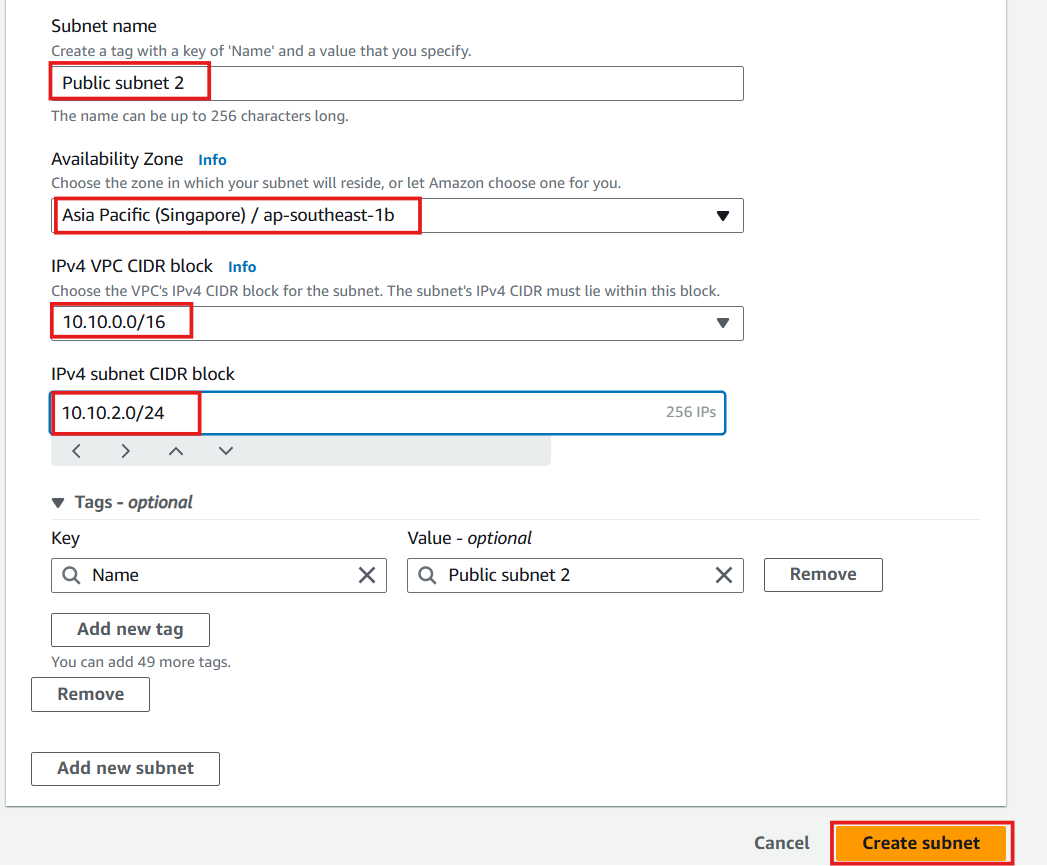
- Public Subnet 2:
- CIDR:
10.10.2.0/24 - Availability Zone: ap-southeast-1b
- CIDR:
- Public Subnet 2:
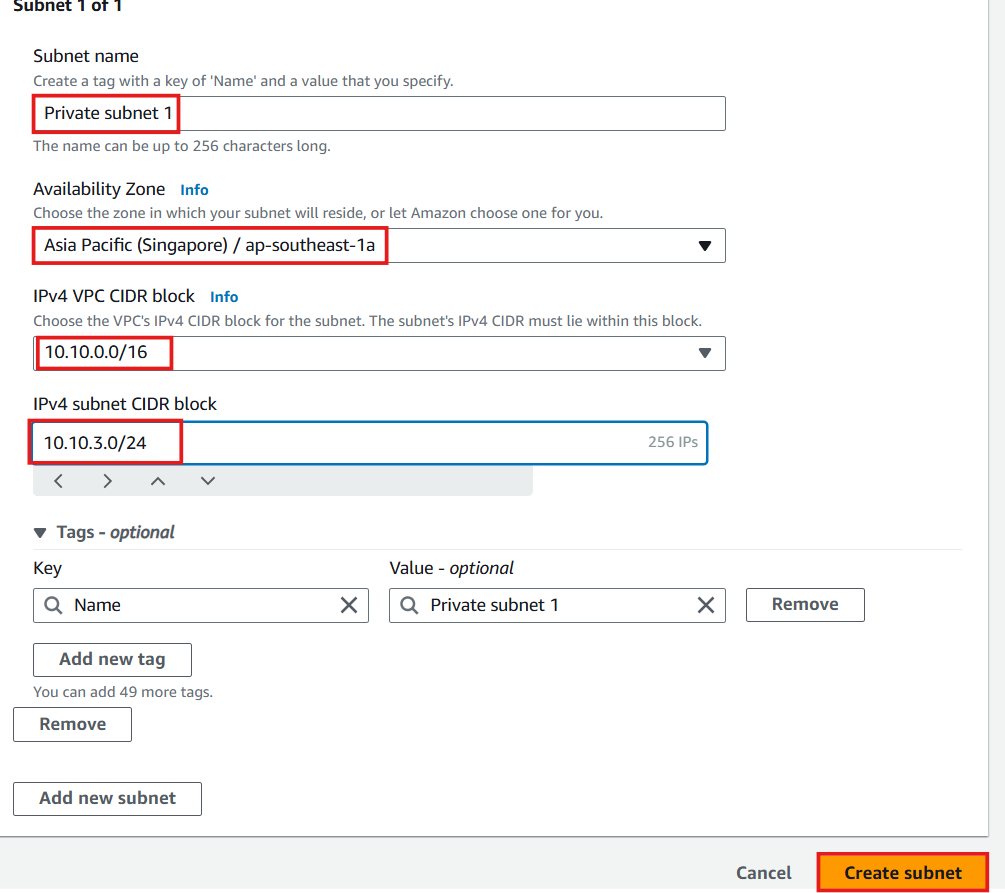
- Private Subnet 1:
- CIDR:
10.10.3.0/24 - Availability Zone: ap-southeast-1a
- CIDR:
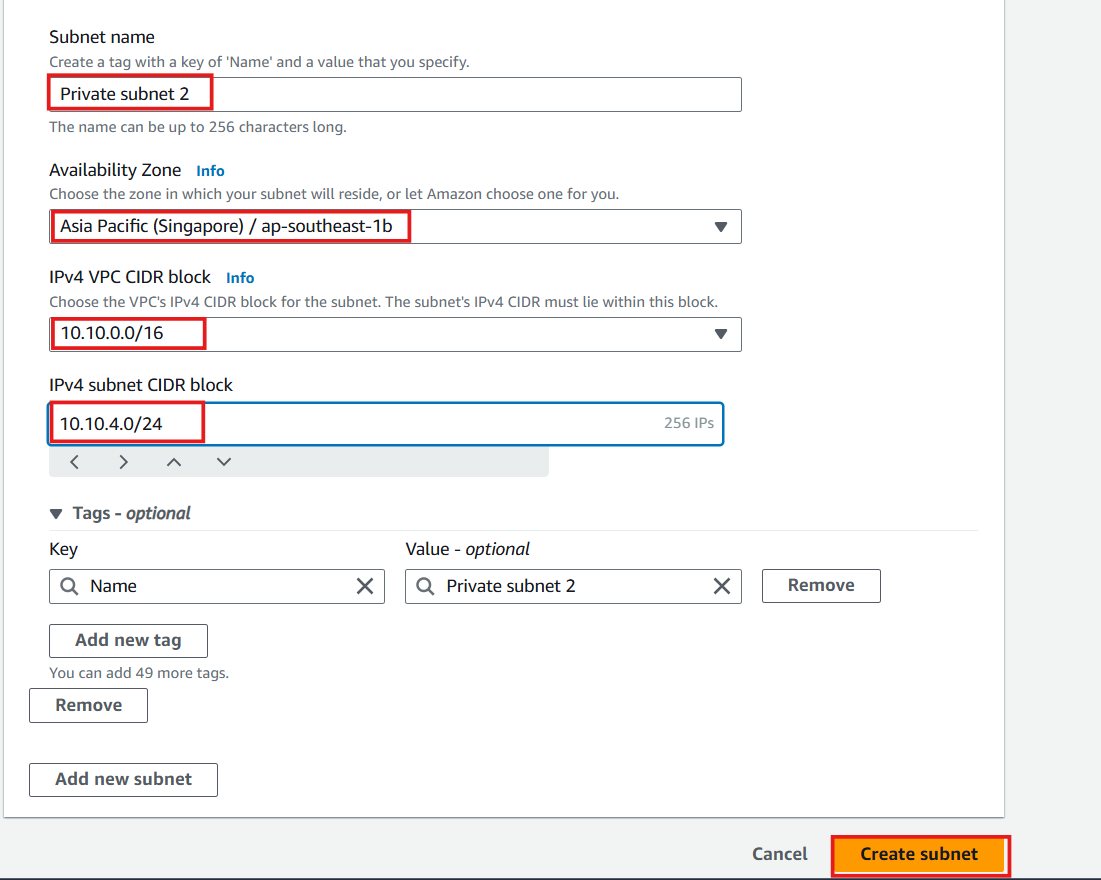
- Private Subnet 2:
- CIDR:
10.10.4.0/24 - Availability Zone: ap-southeast-1b
- CIDR:
💡 Pro Tip
AWS displays both Availability Zone names and Availability Zone IDs in the console. AWS randomly maps AZ names (like ap-southeast-1a) to physical AZ IDs (like apse1-az2) across different AWS accounts to distribute workloads evenly. When designing multi-AZ architectures across accounts, always reference AZ IDs rather than AZ names for consistency.
Configuring Public Subnets
ℹ️ What Makes a Subnet “Public”?
A subnet becomes “public” when it has a route to an Internet Gateway and instances within it can receive public IP addresses. By default, newly created subnets do not automatically assign public IP addresses to instances launched within them.
💡 Pro Tip
The distinction between public and private subnets is determined by routing configuration and IP address assignment, not by any inherent subnet property. Both use the same subnet resource type in AWS.
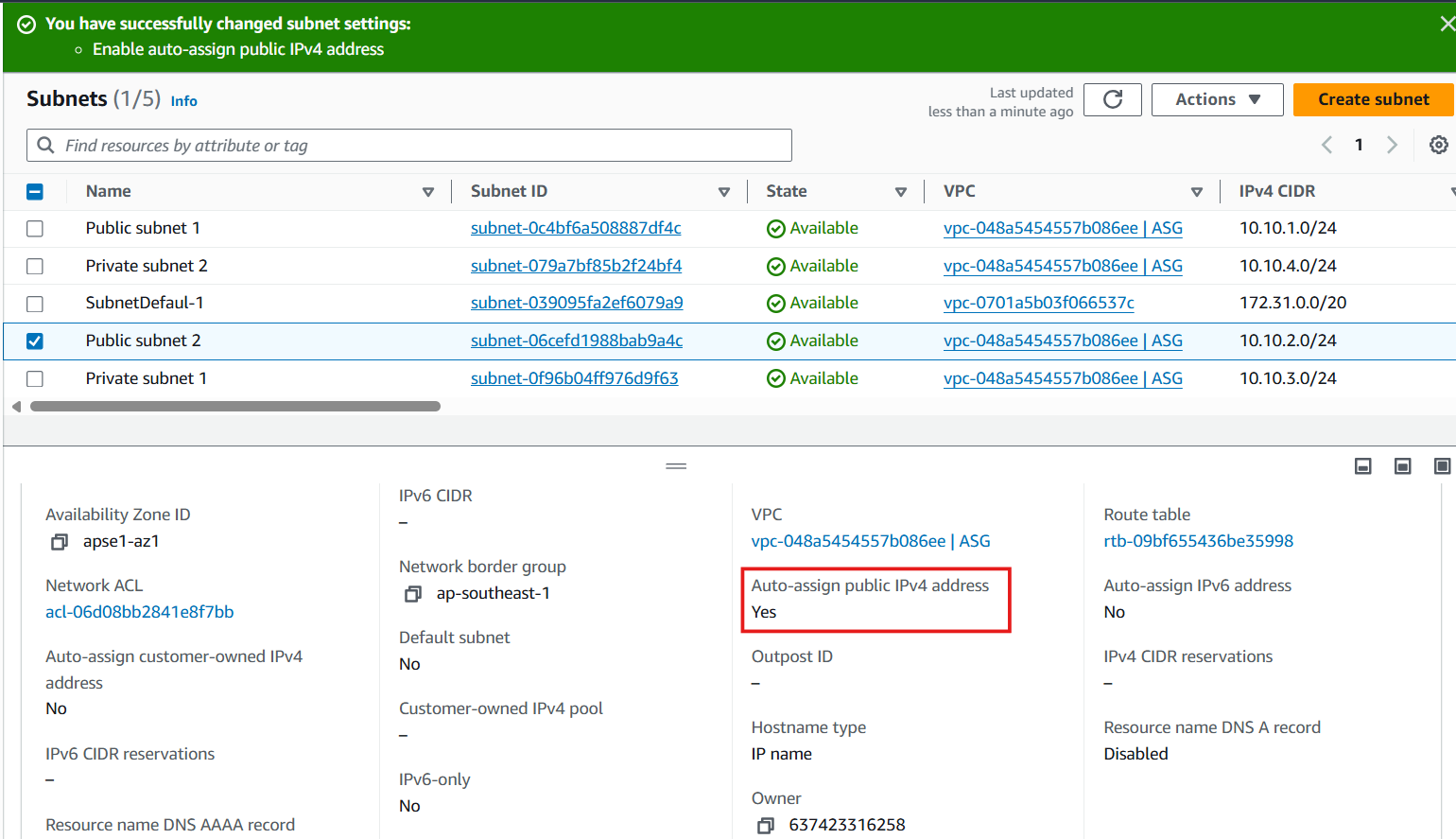
- Enable automatic public IP assignment for public subnets:
- Select Public Subnet 1 from the subnet list
- Click Actions > Edit subnet settings
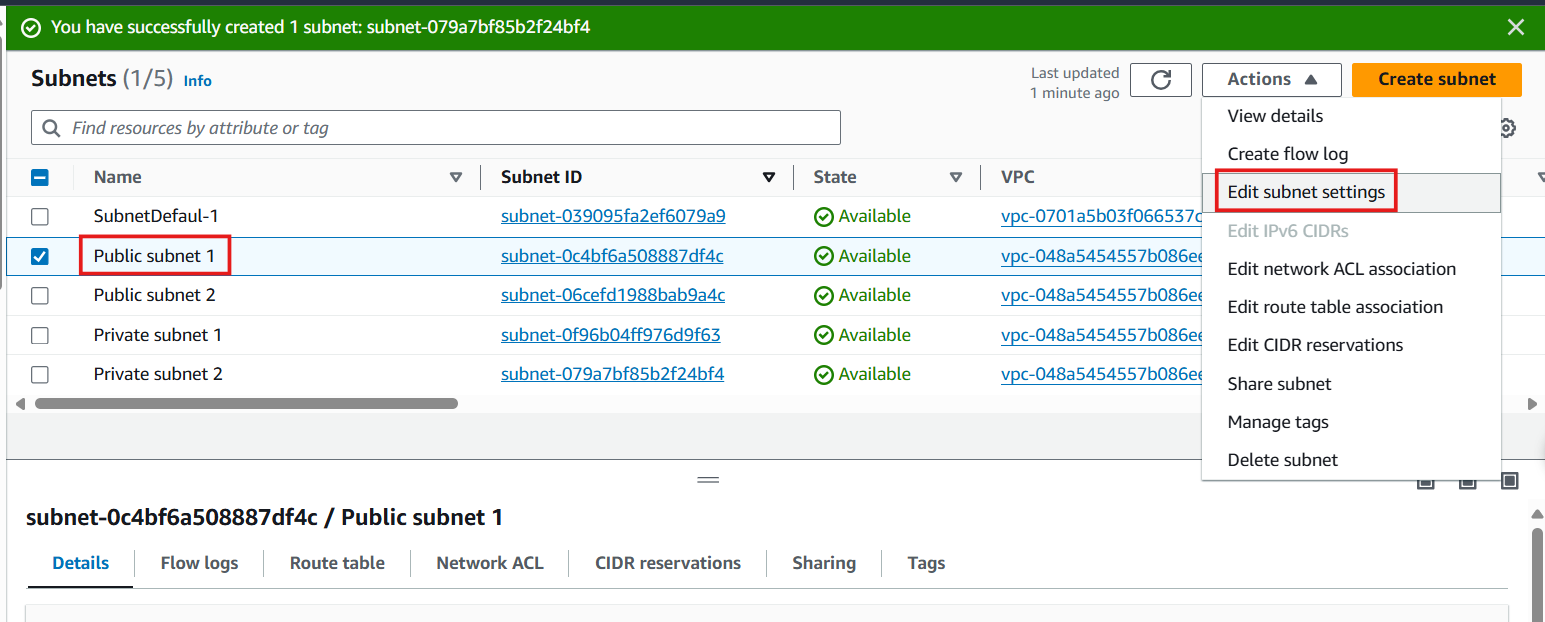
- Configure auto-assign IP settings:
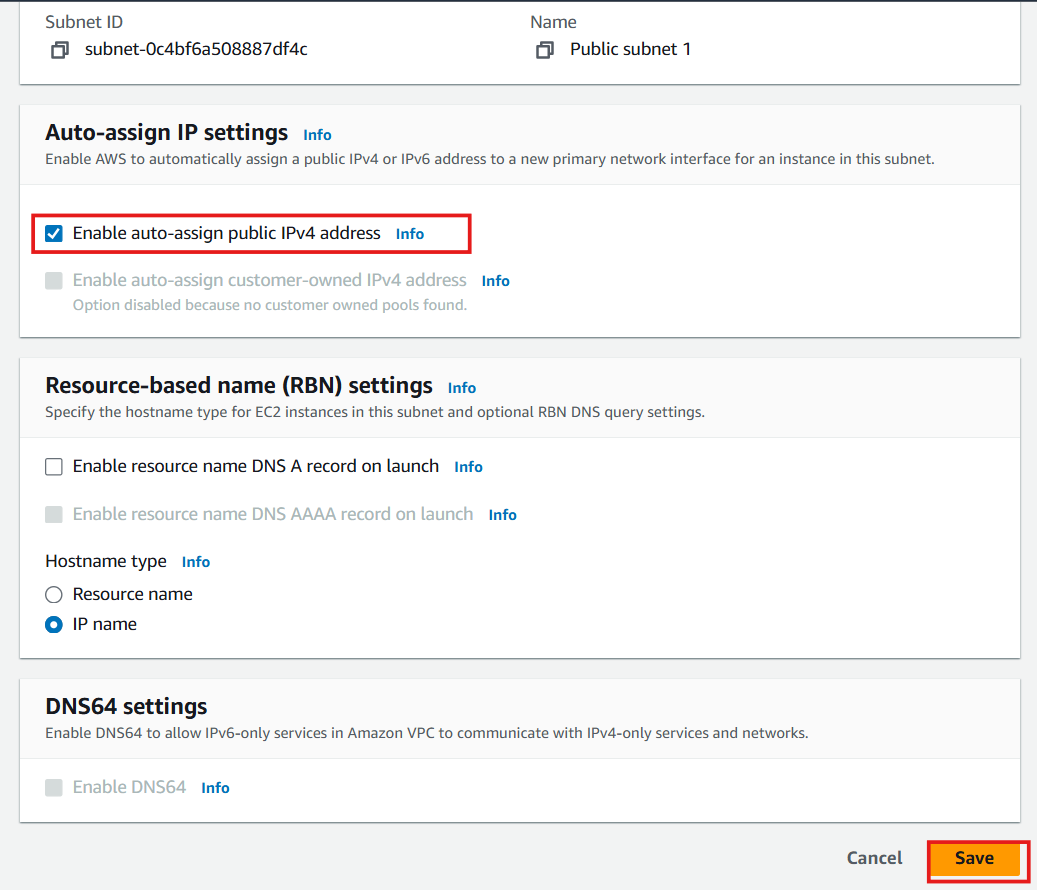
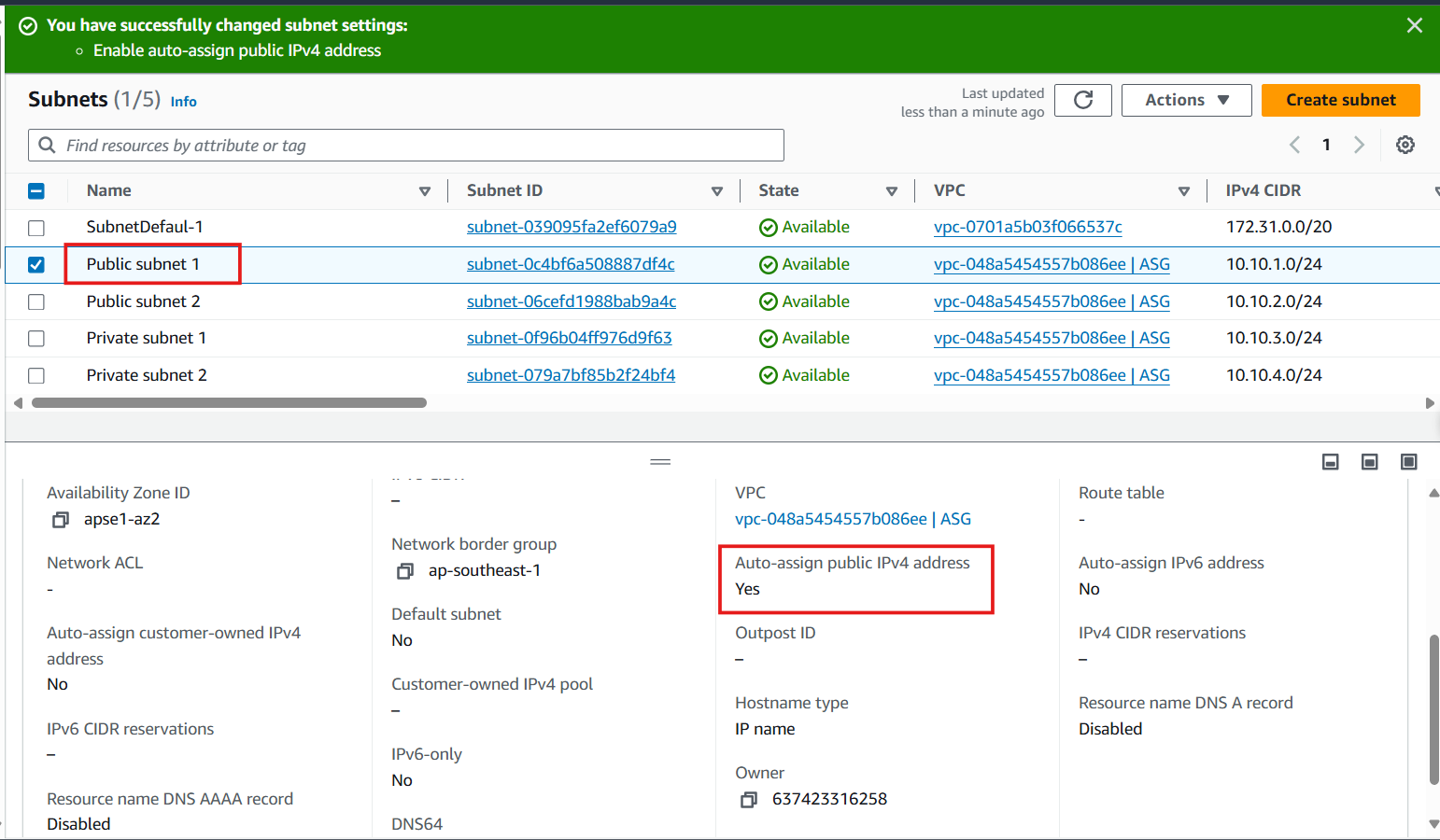
- Under Auto-assign IP settings, check Enable auto-assign public IPv4 address
- Click Save
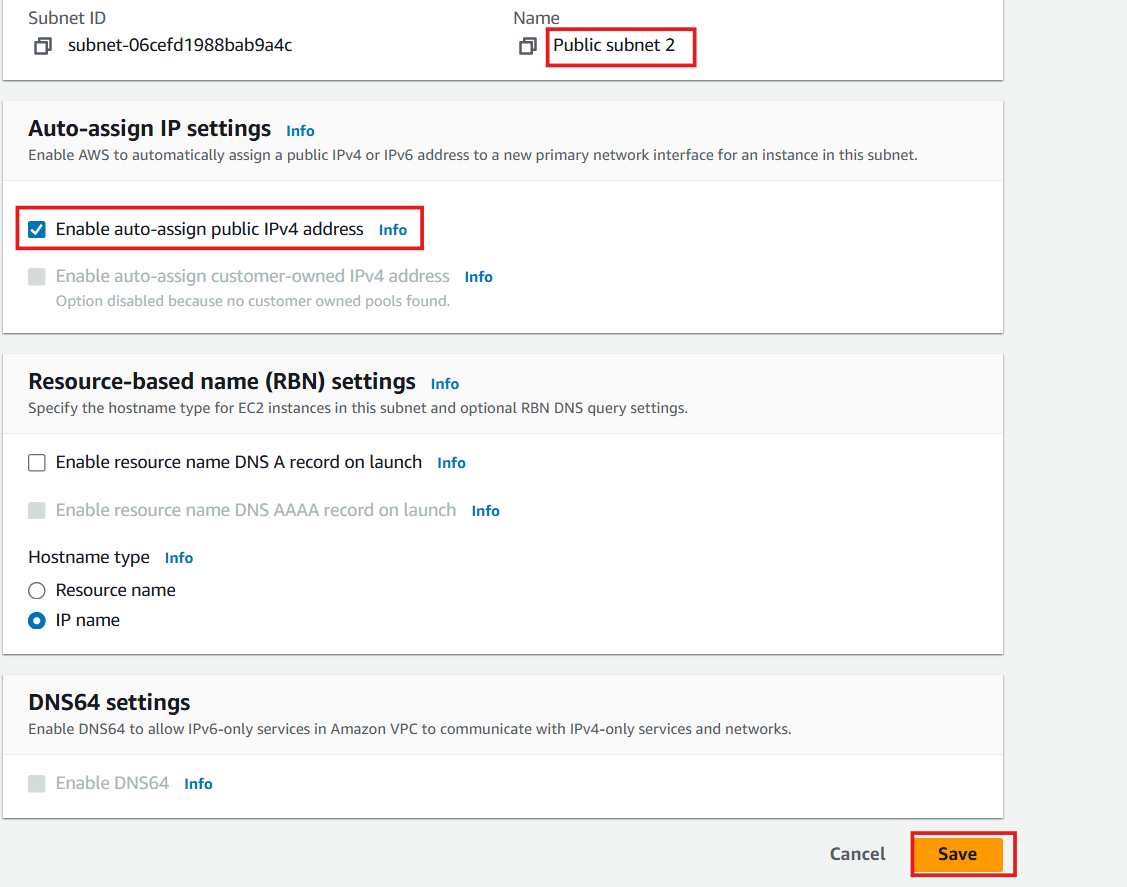
- Repeat the same process for Public Subnet 2:
- Select Public Subnet 2
- Click Actions > Edit subnet settings
- Enable auto-assign public IPv4 address
- Save your changes
⚠️ Important Consideration
While we’ve enabled auto-assign public IP addresses for our public subnets, instances in these subnets will not have internet connectivity until we create and attach an Internet Gateway and configure the appropriate route tables in subsequent steps.